Relationship in queries
အရှေ့အပိုင်းမှာရေးခဲ့တဲ့ one to one, one to many, many to many relationship တွေအကြောင်းကိုအခုအပိုင်းမှာလက်တွေ့ query တွေရေးကြည့်ပြီးထပ်လေ့လာသွားကြပါမယ်။ INNER နဲ့ LEFT JOIN တွေကိုအဓိကထားပြီးသုံးသွားမှာဖြစ်လို့ဘယ်လိုပုံစံမျိုးလိုချင်တဲ့အခါ ဘယ် JOIN ကိုသုံးနိုင်တယ်ဆိုတာမျိုးကိုပါတစ်ပါတည်းမှတ်သွားစေချင်ပါတယ်။
One to one
Query တွေစမ်းပြီးရေးကြည့်ဖို့အတွက် students နဲ့ student_detailstable နှစ်လုံးကိုအသုံးပြုပါမယ်။ student တစ်ယောက်မှာ detail info တစ်ခုသာရှိနိုင်ပါတယ်။ (One to one relationship type)
students table ထဲမှာရှိတဲ့ records တွေကိုသက်ဆိုင်ရာ student_details records တွေနဲ့အတူ JOIN လုပ်ပြီးဆွဲထုတ်ကြည့်ပါမယ်
SELECT students.student_id, students.name, student_details.address FROM students JOIN student_details ON students.student_id = student_details.student_id;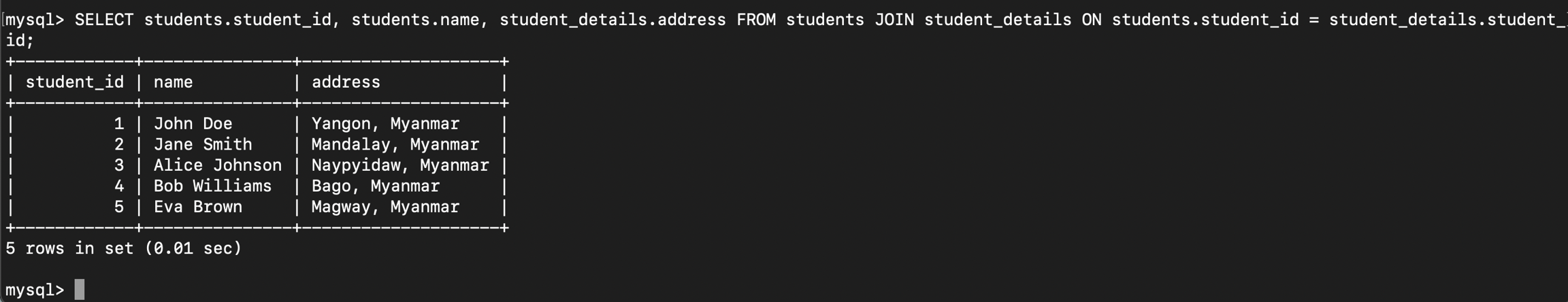
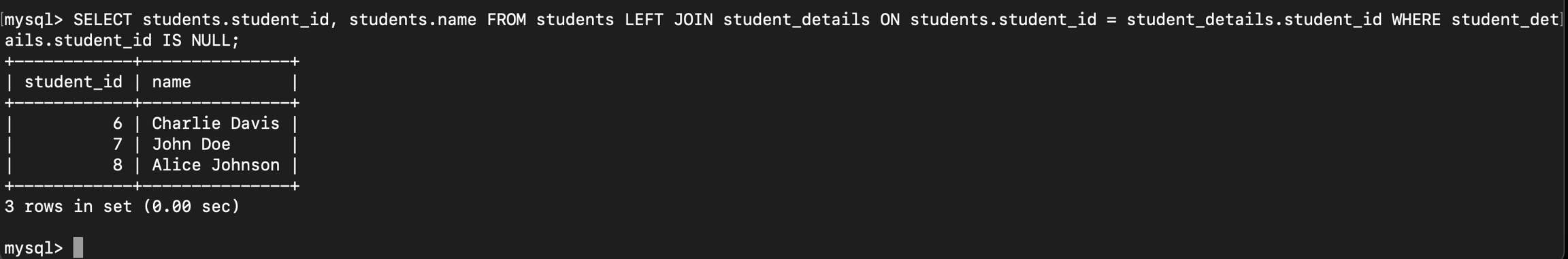
student_details ဘက်မှာ records မရှိတဲ့ students တွေကိုထုတ်ကြည့်ပါမယ်။
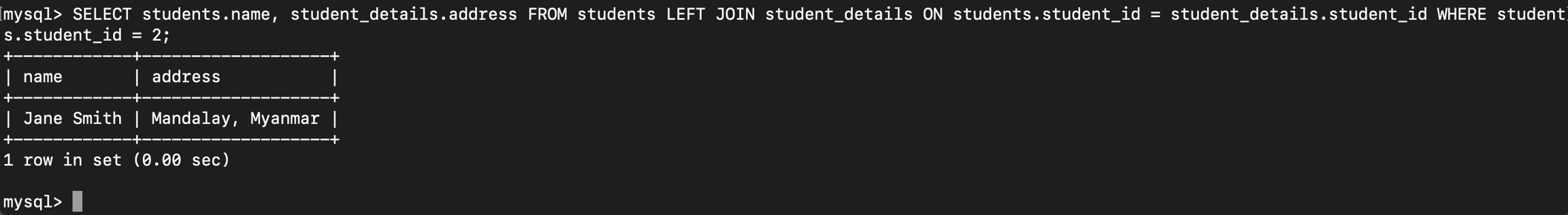
students တစ်ယောက်တည်းကိုပဲသူ့ရဲ့ details record နဲ့အတူဆွဲထုတ်ကြည့်ပါမယ်။
One-to-Many Relationship:
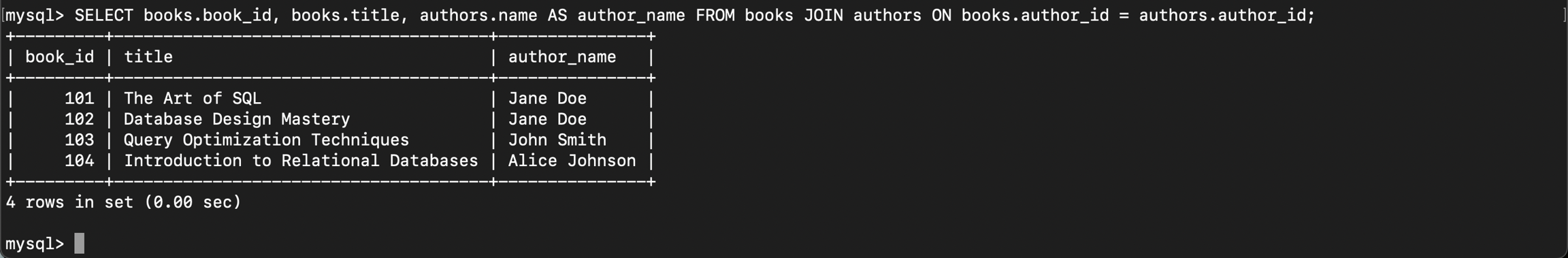
Relationship အပိုင်းမှာတုန်းက create လုပ်ခဲ့တဲ့ authors နဲ့ books table ကိုအသုံးပြုပါမယ်။ authors တစ်ယောက်မှာရေးခဲ့တဲ့ books တွေအများကြီးရှိနိုင်တယ်ဆိုတဲ့ one to many relationship ပုံစံဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ Table အလွတ်တွေဖြစ်တဲ့အတွက် data တွေအရင်ထည့်ပါမယ်။


စာအုပ်တွေကိုဆွဲထုတ်ရင်းတစ်ပါတည်းရေးခဲ့တဲ့ author တွေကိုပါထုတ်ကြည့်ပါမယ်။
စာအုပ်မရေးဖူးတဲ့ author record ကိုဆွဲထုတ်ကြည့်ပါမယ်။

လောလောဆယ်သွင်းထားတဲ့ data အရ စာအုပ်မရေးထားတဲ့ author record မရှိတဲ့အတွက်ကြောင့် author record အသစ်တစ်ကြောင်းထည့်ကြည့်ပြီး query ကိုပြန် run ကြည့်ပါမယ်။
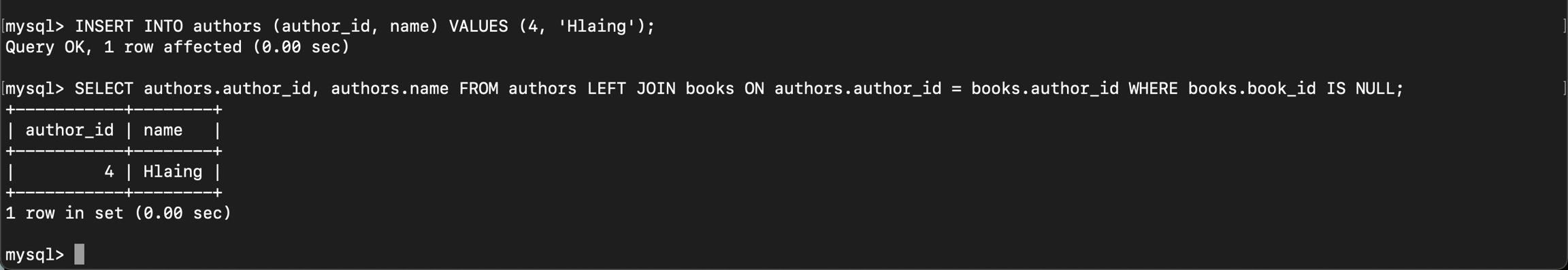
book record မရှိတဲ့ author တစ်ယောက်ဖန်တီးလိုက်ပါပြီ။ Query ကိုပြန် run ကြည့်မယ်ဆို book record reference မရှိတဲ့ author record ကိုမြင်ရမှာဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
Many-to-Many Relationship:
students တစ်ယောက်မှာ courses တွေအများကြီးရှိနိုင်သလို courses တစ်ခုမှာလည်း students အများကြီးရှိနေနိုင်တဲ့ many to many relationship type ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ Table အလွတ်တွေဖြစ်တဲ့အတွက်ထုံးစံအတိုင်း data တွေအရင်ထည့်ပါမယ်။

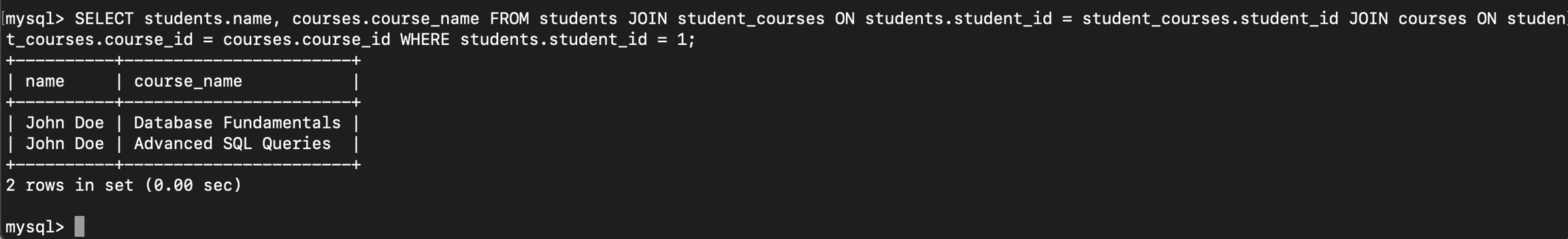
student_id 1 ဖြစ်တဲ့ကျောင်းသားကဘယ်လို courses တွေယူထားလဲဆိုတာဆွဲကြည့်ရအောင်။ Many to many relation ဖြစ်တဲ့ဒီနေရာမှာ junction table တစ်ခုခံထားတဲ့အတွက် JOIN ကနှစ်ခါဖြစ်သွားတာကိုသတိချပ်ထားရပါမယ်။
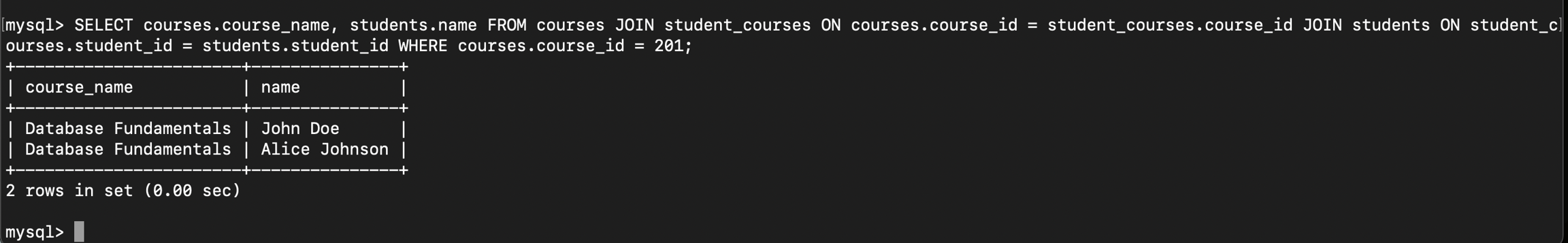
course_id 201 မှာတက်ရောက်နေတဲ့ students တွေကိုလည်းထုတ်ကြည့်နိုင်ပါတယ်။
students ရော courses တွေရောအားလုံးကိုဆွဲထုတ်ကြည့်ပါမယ်။ courses တွေတက်ရောက်ထားခြင်းမရှိတဲ့ကျောင်းသားတွေတော့ COALESCE ဆိုတဲ့ function ကိုသုံးပြီးတော့ course_name နေရာမှာ No Courseဆိုတဲ့စာသားတစ်ခုအစားထိုးထည့်ပေးလိုက်ပါမယ်။
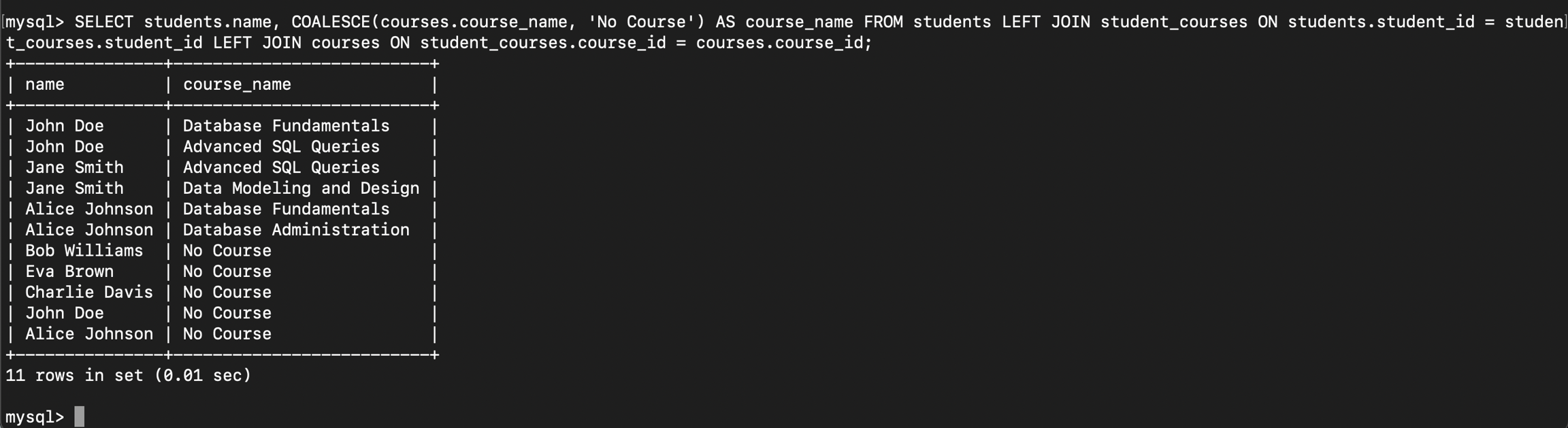
ဒီအပိုင်းထိရောက်လာပီဆိုရင် query တွေနည်းနည်းအဆင့်မြင့်လာတာနဲ့အတူသူတို့ရဲ့ complexity ရှုပ်ထွေးမှုအပိုင်းလေးတွေကိုပါအနည်းငယ်ခံစားလာရမှာဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ သို့ပေမယ့် အရှေ့နှစ်ပိုင်းမှာရေးခဲ့တဲ့ relationship types , joins တွေအကြောင်းကိုသေချာလိုက်လုပ်ထားမယ်ဆို ဒီအပိုင်းကိုလည်းလိုက်နိုင်မယ်လို့ထင်ပါတယ်။ စာသိပ်မလိုက်နိုင်ဘူးဆို relationship နဲ့ join အပိုင်းကို revision ပြန်လုပ်ပြီးပြန်ဖတ်ပါလို့တိုက်တွန်းချင်ပါတယ်။
Last updated